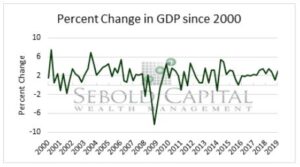
 Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the broadest measure of economic activity within a country and measures the market value of all final goods and services produced within a country over a certain period. There are four components GDP is created from: investment (including residential and nonresidential expenditures), consumption (including durable goods, non-durable goods, and services spending), government spending, and net exports (a country’s total exports minus its total imports).
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the broadest measure of economic activity within a country and measures the market value of all final goods and services produced within a country over a certain period. There are four components GDP is created from: investment (including residential and nonresidential expenditures), consumption (including durable goods, non-durable goods, and services spending), government spending, and net exports (a country’s total exports minus its total imports).
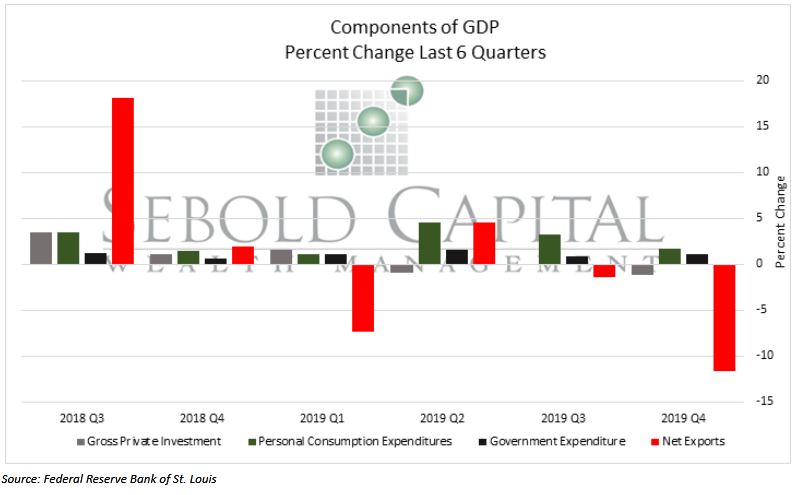
Real GDP increased by 2.1% in the fourth quarter of 2019. Business investments have fallen from –0.1% to –1.2% in the last quarter. Personal consumption expenditures are up 1.7%, which is 1.5% less than the previous 2019 quarter growth of 3.2%. Government expenditures have risen from 0.8% to 1.1%. Net exports have fallen dramatically by -11.6%, after continuously declining from the 2019 third quarter percentage of -1.5%.
The sharp drop in net exports in Q1 of 2019 might have been due to repercussions and concerns about the trade war with China, which began to rebound slightly in Q2 but has further declined sharply from Q3 to Q4. The second quarter saw a drop in private investment, which has continued to fluctuate inconsistently from Q1 to Q4. This fluctuation reflects skepticism in the economic outlook, most likely an effect of trade uncertainty restraining manufacturing and spending activities, as well as other concerns surrounding risks abroad. Consumer spending, which is the largest component of GDP, has declined since Q3 into Q4 of 2019. This decline in consumption may be an effect of rising CPI components such as medical care and energy, which had a Q4 average growth of 0.5% and 0.6%.
February 28, 2020